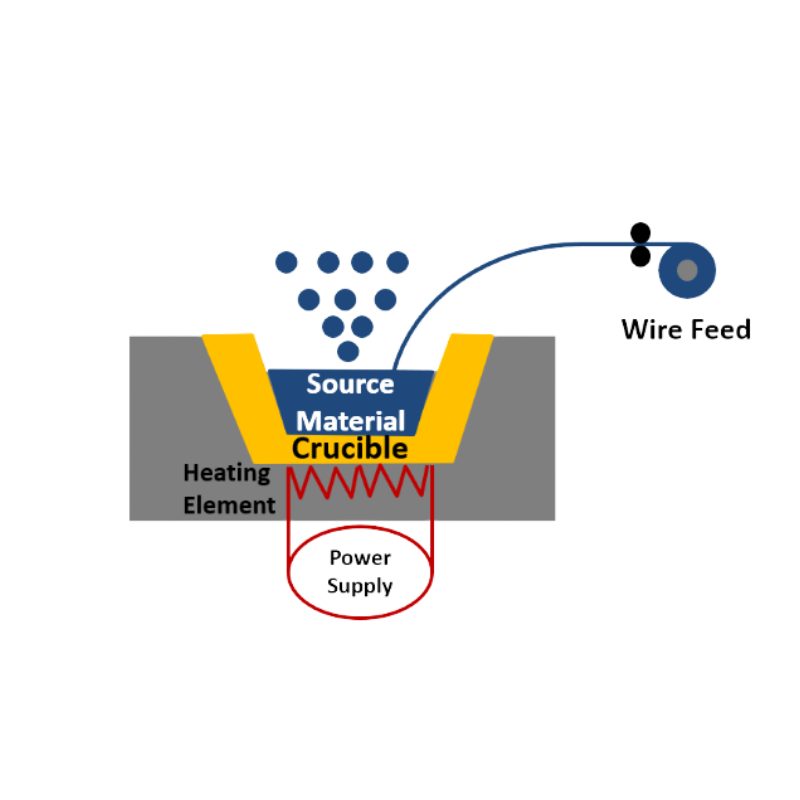
The electron beam evaporation method is a kind of vacuum evaporation coating, which uses electron beams to directly heat the evaporation material under vacuum conditions, vaporize the evaporation material and transport it to the substrate, and condense on the substrate to form a thin film. In the electron beam heating device, the heated substance is placed in a water-cooled crucible, which can avoid the reaction between the evaporation material and the crucible wall and affect the quality of the film. Multiple crucibles can be placed in the device to achieve simultaneous or separate evaporation and deposition of various substances. With electron beam evaporation, any material can be evaporated.
Electron beam evaporation can evaporate high-melting point materials. Compared with general resistance heating evaporation, it has higher thermal efficiency, higher beam current density, and faster evaporation speed. Film and film of various optical materials such as conductive glass.
The characteristic of electron beam evaporation is that it will not or rarely cover the two sides of the target three-dimensional structure, and usually only deposits on the target surface. This is the difference between electron beam evaporation and sputtering.
Electron beam evaporation is commonly used in the field of semiconductor research and industry. The accelerated electron energy is used to strike the material target, causing the material target to evaporate and rise. Eventually deposited on the target.
Post time: Dec-02-2022